Securing the distribution of medicines represents an unprecedented challenge for public health. Although France has always benefited from a particularly secure drug distribution system and a strict legislative framework from the health authorities, the risk of falsified drugs is increasing on a global and European scale.
Faced with this major challenge, Directive 2011/62/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of June 8, 2011 introduced the serialization system, which details were subsequently specified by Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2016/161 of October 2, 2015, in order to strengthen the safety of the distribution chain of medicinal products and to fight against their falsification. The obligations relating to the serialization of medicinal products and anti-counterfeiting devices are applicable since February 9, 2019.
Now 4 years after the entry into force of the European regulation, let’s look back at the implementation of the serialization system.
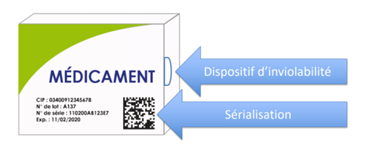
As a reminder, the serialization device is composed as follows:
- A tamper-evident device for all drugs, affixed by the manufacturer and verified by the pharmacist to check the integrity of the product before dispensing (e.g. transparent adhesive tape);
- A unique identifier (UI) on each box of mandatory prescription medication, affixed by the manufacturer and scanned by the pharmacist before dispensing to the patient (datamatrix).
The serialisation system contributes to the implementation of a European system to fight against the introduction of falsified medicines by providing additional security to guarantee the authenticity, safety and quality of medicines on the territory of the European Union. It completes the existing batch traceability by authenticating each box at the time of dispensing.
The implementation of this system required the collective commitment of all the stakeholders in the drug supply chain (manufacturers (CMOs) and Exploitants/Marketing Authorization Holders, wholesalers and distributors, pharmacies and hospitals, software publishers, etc.), as well as the Ministry of Solidarity and Health, the French National Agency for the Safety of Medicines and Health Products (ANSM) and the regional health agencies (ARS).
Indeed, this new system has required organizational changes at all levels, from drug production to delivery to the patient: adapting production lines to implement the unique identifier and the anti-tampering device, adapting the IT systems of all drug professionals, setting up governance bodies at national (NMVO) and European (EMVO) level, adapting procedures, etc.
The question of ultimate responsibility for implementing serialization has been the subject of numerous debates, which have now been settled, with the central issue of downloading unique identifiers at the time of manufacture and the possible outsourcing of this activity. The introduction of the OBP portal registration requirement and fees to finance the infrastructure of national (NMVS) and European (EMVS) repositories systems has also had an impact on the drug chain stakeholders.
WHAT ABOUT THE IMPLEMENTATION OF SERIALIZATION IN PHARMACIES IN FRANCE?
Serialisation is a regulatory obligation for all pharmacies. Indeed, such a system can only operate with the participation of all pharmacies in the Member States in order to ensure that no falsified box is delivered to a patient in the European Union.
This obligation, which came into force on February 9, 2019, was reminded in the Order of February 26, 2021 on good dispensing practices for medicinal products in order to make the obligations incumbent on all pharmacists under European regulations more visible in a text of national scope.
However, to date, despite the health crisis and the strong mobilization of pharmacists, the connection of pharmacies to the system has been delayed and remains insufficient in France. As of February 6, 2023, only 17,901 pharmacies (86.2%) were complying with their obligations to serialize their medicines, with a target of 100% by December 31, 2022.
Given France’s considerable delay in implementing effective verification of the serialization system in pharmacies, a bill was adopted by the Senate on December 14, 2022, defining the financial penalties that may be imposed on pharmacy holders in the event of non-compliance with the obligation to deactivate the unique identifier.
On the page dedicated to serialisation in pharmacies on its website, the Ministry of Health stresses the importance of reaching this 100% objective as soon as possible to guarantee better safety and traceability of medicines for all French people.
Article written by Amélie NICOLAS-VERLEY, Regulatory and Pharmaceutical Affairs Advisor

